Understanding Your Options
Abnormalities in the menstrual cycle are common. Bleeding in any of the following situations is abnormal:
- Bleeding between periods
- Bleeding after sex
- Spotting anytime in the menstrual cycle
- Bleeding heavier or for more days than normal
- Bleeding after menopause
- Menstrual cycles that are longer than 35 days or shorter than 21 days are abnormal. The lack of periods for 3–6 months (amenorrhea) also is abnormal.
Based on your symptoms, laboratory or imaging tests may be ordered to help determine the cause of the abnormal bleeding. It may be helpful to keep track of your menstrual cycle before your visit. Note the dates, length, and type (light, medium, heavy, or spotting) of your bleeding on a calendar.
Fibroids
Also known as leiomyomas, fibroids are benign tumors originating from uterine tissue. They can vary greatly in size and number. They are very common and most of the time they do not cause bothersome symptoms and go undetected. However, 1 in 4 women end up with symptoms severe enough to require treatment. Symptomatic patients may experience heavy bleeding, irregular bleeding, painful periods, as well as pelvic pressure and urinary frequency from an enlarged uterus.
Fibroids can be located inside the cavity of the uterus (submucosal), within the wall of the uterus (intramural), or on the surface of the uterus (subserosal). Symptoms will vary depending on the location and size of the fibroid(s).
Polyps
Endometrial (intrauterine) polyps are one of the most common causes of abnormal bleeding in both premenopausal and postmenopausal women, though many women with polyps have no symptoms. The great majority of polyps are non-cancerous, but malignancy occurs in some women. They are caused by overgrowths of endometrial glands that form a projection from the endometrium and can develop anywhere in the cavity of the uterus.
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is an abnormal location of uterine lining cells that develops inside the uterine walls. It causes pelvic pain and heavy bleeding. Adenomyosis prevents effective uterine contractions during a period, making it more painful and prolonged. Fibroids and adenomyosis may coexist in the same uterus. This may exacerbate already severe symptoms.
Medical Treatment
Hormonal medications often are used to control abnormal uterine bleeding. Birth control pills can help make your periods more regular. Hormones also can be given as an injection, an implant, or through an intrauterine device (IUD) that releases a hormone (Progesterone.) An IUD is a birth control device that is inserted in the uterus. The hormones in the IUD are released slowly and may control abnormal bleeding.
Other medications given for abnormal uterine bleeding include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (such as ibuprofen), tranexamic acid, and antibiotics (if there is an infection).
Endometrial Ablation
Uterine Endometrial Ablation is one of the most effective options for persistent, prolonged and heavy uterine bleeding. Endometrial ablation destroys the lining of the uterus using thermal (heat) energy or a freezing technique. The procedure is ideal for patients who do not desire major surgery and are no longer interested in future pregnancy. It is an excellent alternative to hysterectomy.
Dr. Rebeles offers NovaSure endometrial ablation, a one-time, 5-minute procedure that can lessen or stop your heavy period altogether, without on-going pills and without hormonal side effects. For over 90% of women, menstrual bleeding is dramatically reduced or stopped. It works by removing the endometrium, or the lining of the uterus (the part that causes the bleeding), with a quick delivery of radio-frequency energy. There are other types of endometrial ablation that may be more appropriate for patients depending on their particular condition.
NovaSure endometrial ablation procedure steps and how it works:
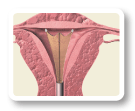
Your doctor slightly opens your cervix (the opening to the uterus), inserts a slender wand, and extends a triangular mesh device into the uterus
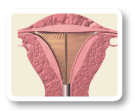
The mesh gently expands, fitting to the size and shape of your uterus
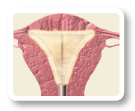
Precisely measured radio frequency energy is delivered through the mesh for about 90 seconds
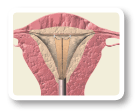
The mesh device is pulled back into the wand, and both are removed from the uterus.
No part of the NovaSure endometrial ablation device remains inside your body after the NovaSure procedure.
Dilation and Curettage
A dilation and curettage (D&C) is an outpatient procedure designed to immediately stop severe, sometimes life-threatening bleeding, or to diagnose the cause of bleeding with a sample of tissue from the lining of your uterus (endometrium). This procedure helps diagnose uterine cancer, uterine polyps and endometrial hyperplasia — a precancerous condition in which the uterine lining becomes too thick.
Hysteroscopic Myomectomy and Polypectomy
Hysteroscopy is an outpatient minimally invasive procedure designed to remove uterine fibroids or polyps located in the uterine cavity that may be the cause of abnormal bleeding. The ultimate goal of the procedure is complete cessation of abnormal bleeding and inspection of the tissue removed to rule out the presence of cancer. This procedure is an outpatient procedure. Hysteroscopy is accomplished by inserting a long tubular camera scope called a hysteroscope through the cervix into the uterus, then inserting various instruments to remove polyps or fibroids.
Dr. Rebeles utilizes the Myosure Tissue Removal System, a hysteroscopic outpatient procedure that can eliminate fibroids or polyps without having to cut or remove any part of your uterus.
Laparoscopic (and Robotic-assisted) Myomectomy:
This procedure is a minimally invasive surgery which removes intramural and subserosal fibroids from the uterus via small abdominal incisions. They require a highly skilled surgeon specializing in minimally invasive surgery. The advantages of a laparoscopic procedure are many. Patients usually go home the same day, the recovery time is faster and less painful, and the cosmetic outcome is better. Dr. Rebeles operates through a few small abdominal incisions using either the assistance of the da Vinci robot or via traditional laparoscopy.
(Please also see: Robotic-Assisted Myomectomy under Robotic Surgery )
Laparoscopic (and Robotic-assisted) Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy refers to the removal of a woman’s uterus (womb) and possibly the cervix. Hysterectomy is one of the most common surgeries in the United States, with approximately 600,000 performed annually. Dr. Rebeles operates through a few small abdominal incisions using either the assistance of the da Vinci robot or via traditional laparoscopy.
Total (or complete) hysterectomy involves the removal of the entire uterus, but not necessarily the ovaries
Partial, subtotal and supracervical hysterectomy are all terms to describe removal of the part of the uterus above the cervix, which is the part of the uterus responsible for growing and shedding the endometrial (uterine) lining.
(Please also see: Robotic-Assisted Hysterectomy under Robotic Surgery )
Dr. Rebeles will discuss with you which type of surgery is best for you and the pros and cons of each.










Make an Appointment
Request your next appointment date. Our Scheduling Staff will reply back with all available appointment date and time options that meet your requirements.
*Please Note: Dr. Rebeles does not offer prenatal care.
Additionally, Dr. Rebeles is no longer accepting new patients, effective May 1, 2024.

